Installing R packages
Packages in R (also called libraries) are shared by the R community at large and allow to expand the capabilities of the base R software by many folds. They provide a set of extra R functions around a specific theme like plotting (e.g. ggplot2), date manipulation (e.g. lubridate), statistics (e.g. mgcv), etc. They are great and you will learn to rely on them quickly for day-to-day tasks. You first need to install a package in R to make it available. This is very easy.
In R Studio
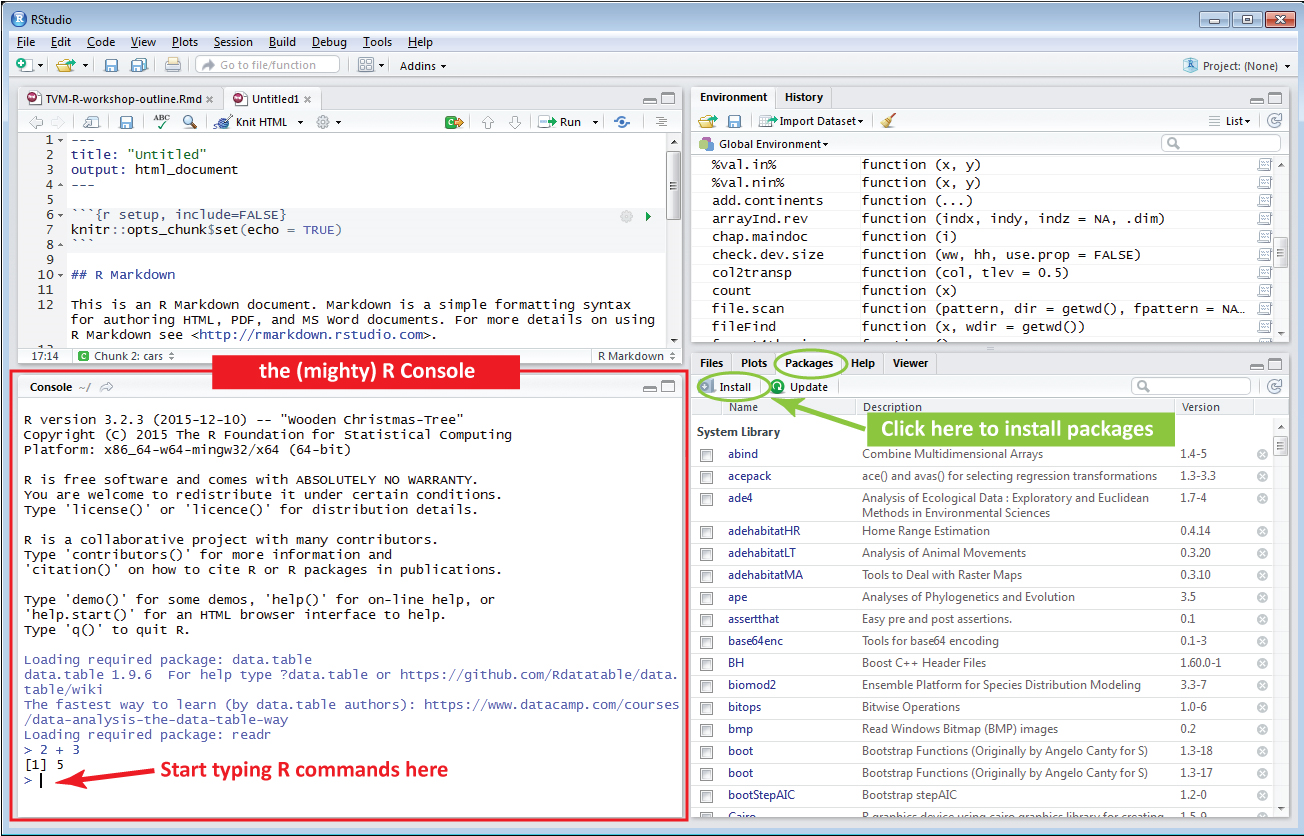
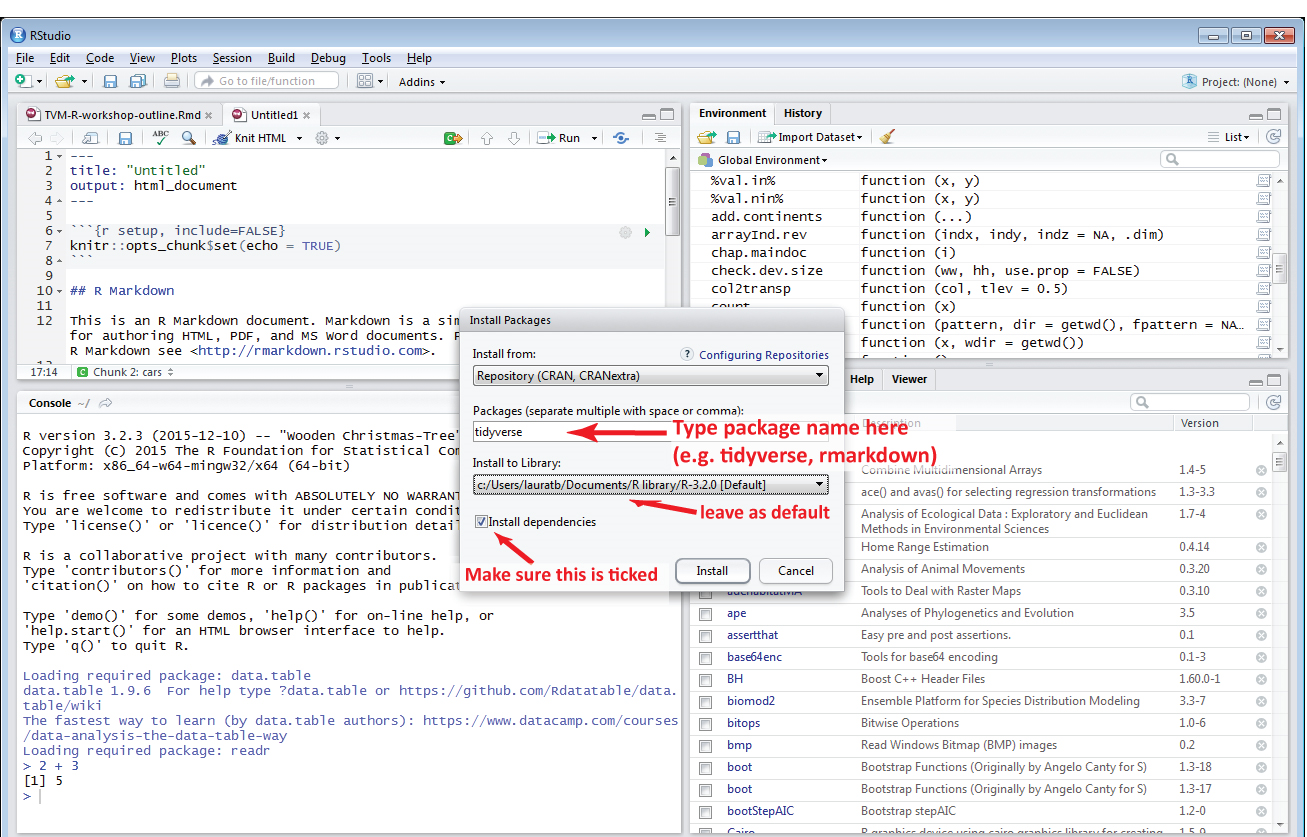
In the console
install.packages('ggplot2')From the .zip
You can find the .zip for R packages on the Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN). Once
install.packages('C:/path/to/your/package/zip/ggplot2.zip', repos=NULL, type='source')Where are my packages installed?
To see where R installs your packages, look at the first item returned by:
.libPaths()If you want R to install packages elsewhere, you can either specify it manually by setting the argument lib when launching install.packages(), or use the R Studio install tool to pick another install location. To change it permanently, have a look here.
Copyright © 2017 Pacific Community. All rights reserved.